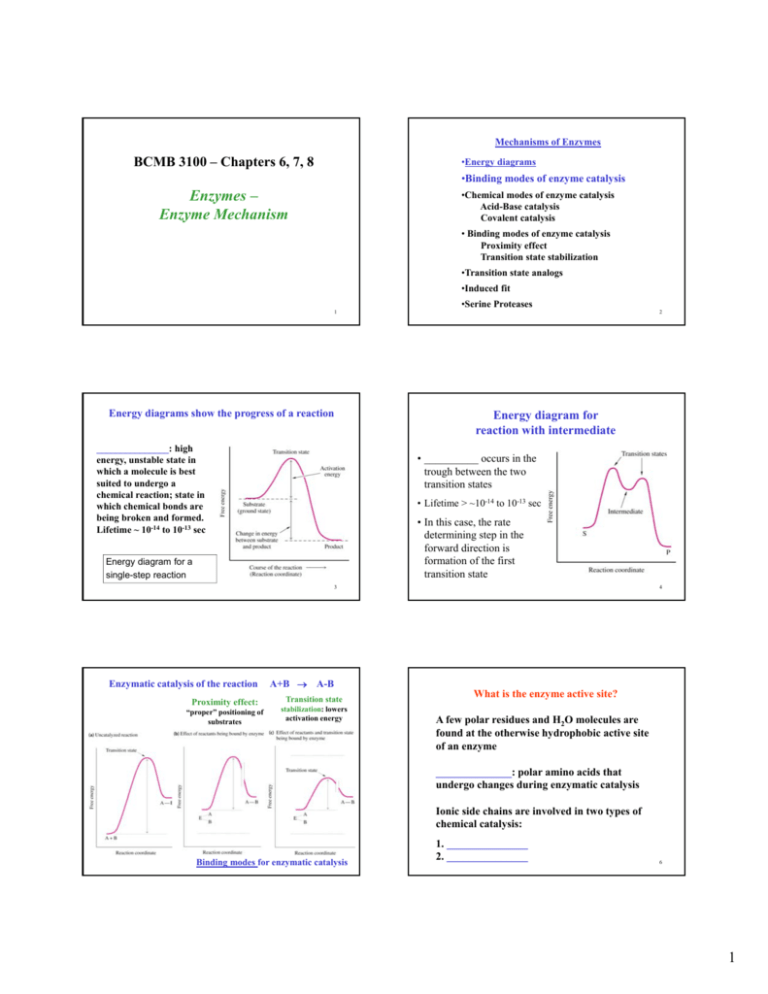
45 2 step reaction energy diagram
Arrhenius Theory and Reaction Coordinates - Chemistry 302 The key is that there are many many potential paths between reactants and products. The reaction coordinate represents the lowest energy path. For example, in the reaction of CH 3 Cl + OH- to form CH 3 OH and Cl-, the mechanism of this reaction is a single step in which the CH 3 Cl collides with the OH- and forms the products. We can envision a ... PDF Potential energy diagram for a two-step sequential reaction Potential energy diagram for a two-step sequential reaction A 1 19 3 50 AB* 4 33 3 40 B 3 28 3 30 BC* 4 41 3 20 C 5 13 3 10 3 0 the red lines are error bars on the x -value Adjust energies Derived from Scott Sinex's Excel chart 1 2 3 4 5 0 10 20 30 40 50 Energy Reaction coordinate step 1 step 2 A B C A B C k 1k 2
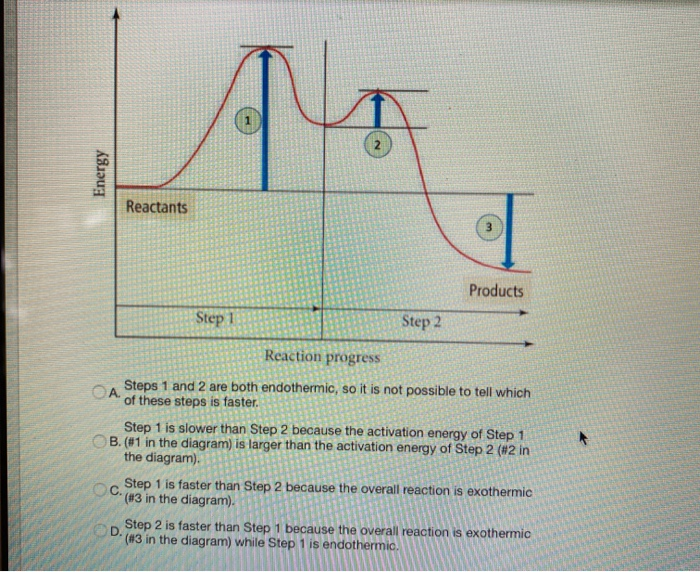
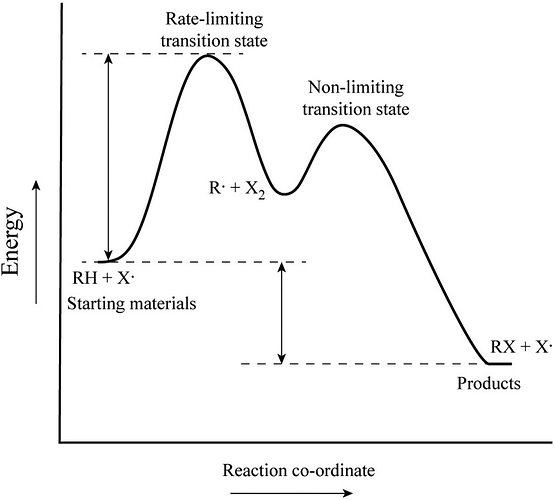
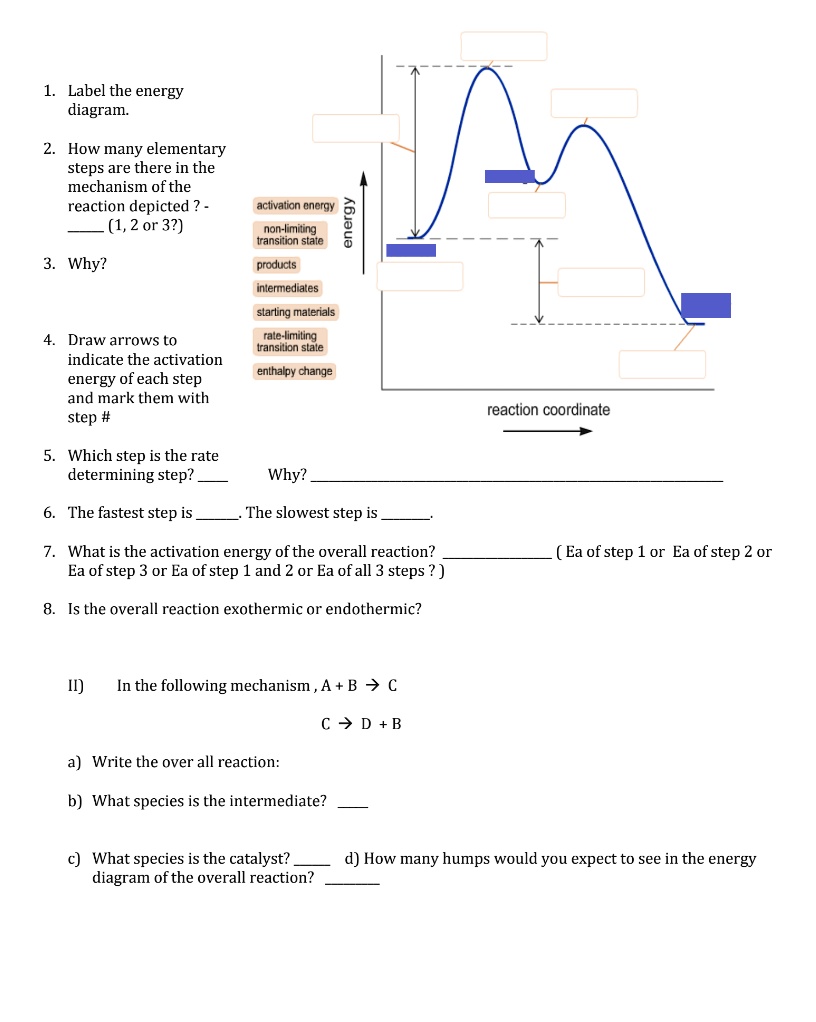
Solved Label the energy diagram for a two-step reaction. - Chegg Question: Label the energy diagram for a two-step reaction. enthalpy change transition state starting materials RX+H products rate-limiting transition state intermediates activation energy reaction coordinate This problem has been solved! See the answer Show transcribed image text Expert Answer 100% (49 ratings)
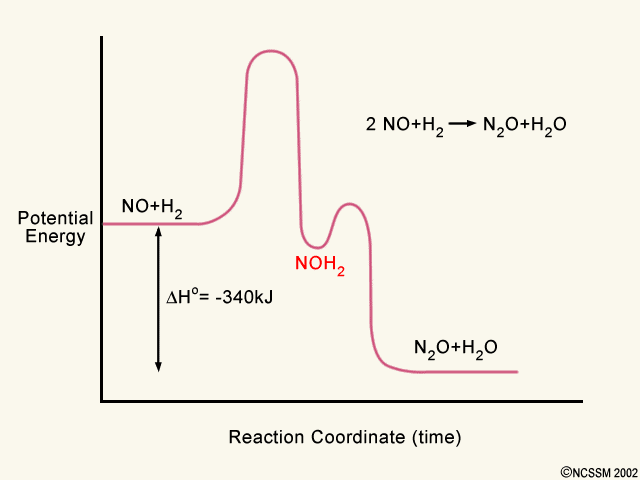
2 step reaction energy diagram
12.7 Catalysis - Chemistry - opentextbc.ca Figure 2. This potential energy diagram shows the effect of a catalyst on the activation energy. ... provides a different reaction path with a lower activation energy. As shown, the catalyzed pathway involves a two-step mechanism (note the presence of two transition states) and an intermediate species (represented by the valley between the two ... 7.4 SN1 Reaction Mechanisms, Energy Diagram and Stereochemistry 7.4 SN1 Reaction Mechanisms, Energy Diagram and Stereochemistry SN1 Reaction Mechanism The reaction between tert -butylbromide and water proceeds via the SN1 mechanism. Unlike S N 2 which is a single-step reaction, S N 1 reaction involves multiple steps. Reaction: (CH 3) 3 CBr + H 2 O → (CH 3) 3 COH + HBr Solved: Sketch an energy diagram for a two-step reaction in which ... 13P Sketch an energy diagram for a two-step reaction in which both steps are exergonic and in which the second step has a higher-energy transition state than the first. Label the parts of the diagram corresponding to reactant, product, intermediate, overall Δ G‡, and overall Δ G °. Step-by-step solution 89% (9 ratings) for this solution Step 1 of 4
2 step reaction energy diagram. SOLVED:Draw a reaction coordinate diagram for a two-step reaction in ... Sketch an energy diagram for a two-step reaction in which both steps are exe… 06:56. Draw an energy diagram for a two-step exergonic reaction whose second step i… 02:12. Draw a graph showing the reaction pathway for an overall exothermic reaction… 01:07. A chemical reaction is endothermic and has an activation energy ... SN2 Reaction Mechanism: Energy Level Diagram ... - Collegedunia The change in energy for the above reaction is represented in the energy level diagram given below. SN2 is a single-step reaction, so the diagram only shows one curve. The lower energy of the products CH 3 OH and Br - compared to the reactants CH 3 Br and OH - suggests that the reaction is exothermic and that the products are more stable. 6.8: Energy Diagram for a Two-Step Reaction Mechanism Recall that the first step of the reaction above, in which two charged species are formed from a neutral molecule, is much the slower of the two steps, and is therefore rate-determining. This is illustrated by the energy diagram, where the activation energy for the first step is higher than that for the second step. Draw a reaction coordinate diagram for a two-step reaction i - Quizlet Draw a reaction coordinate diagram for a two-step reaction in which the first step is endergonic, the second step is exergonic, and the overall reaction is endergonic. Label the reactants, products, intermediates, and transition states. Explanation Verified Reveal next step Reveal all steps Create a free account to see explanations
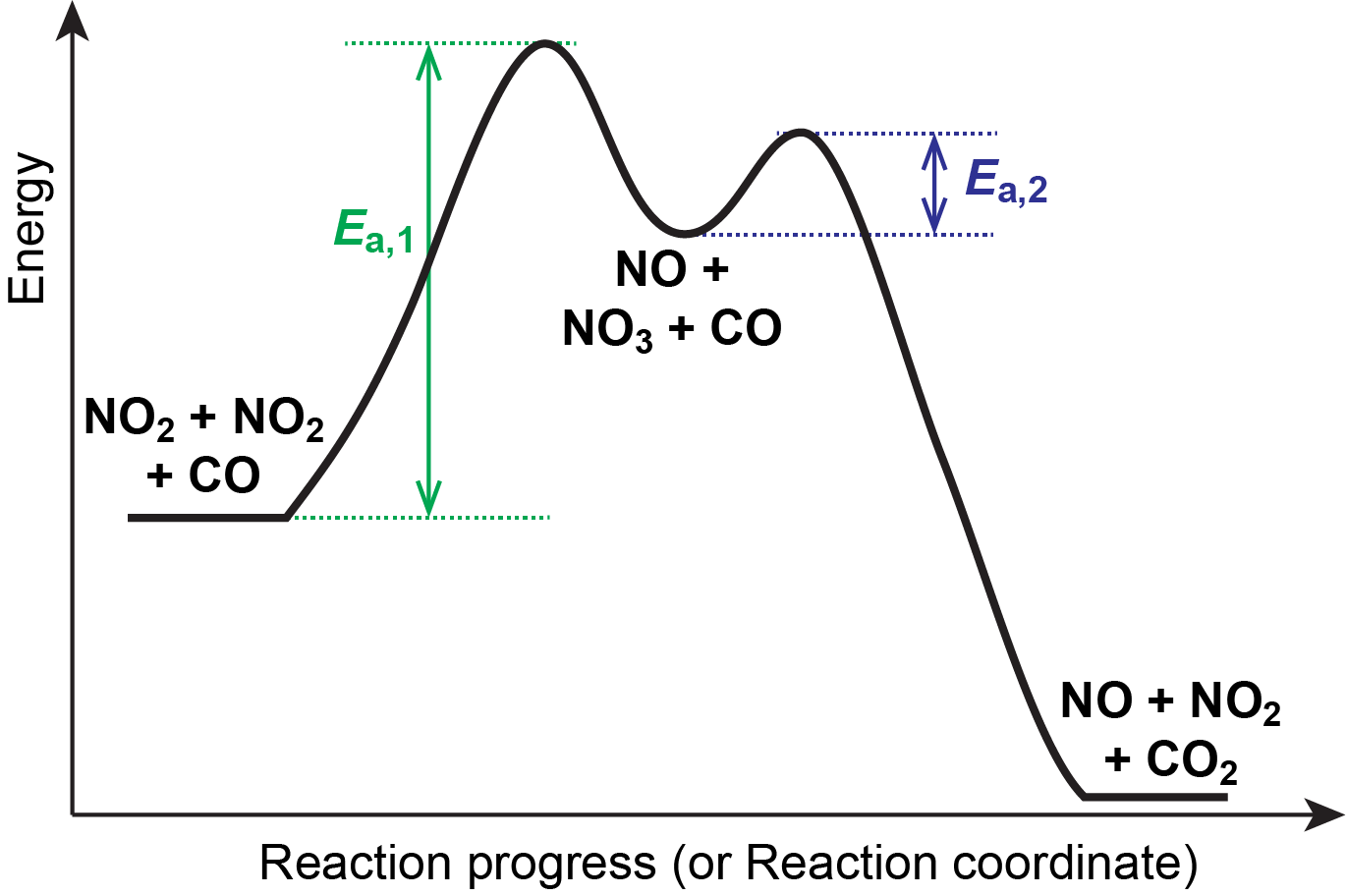
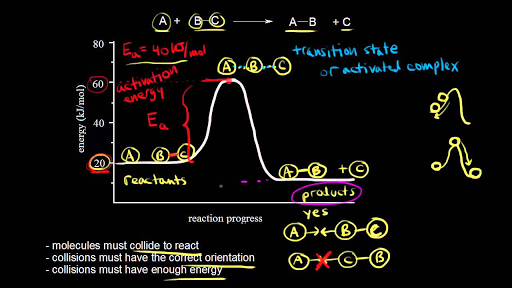
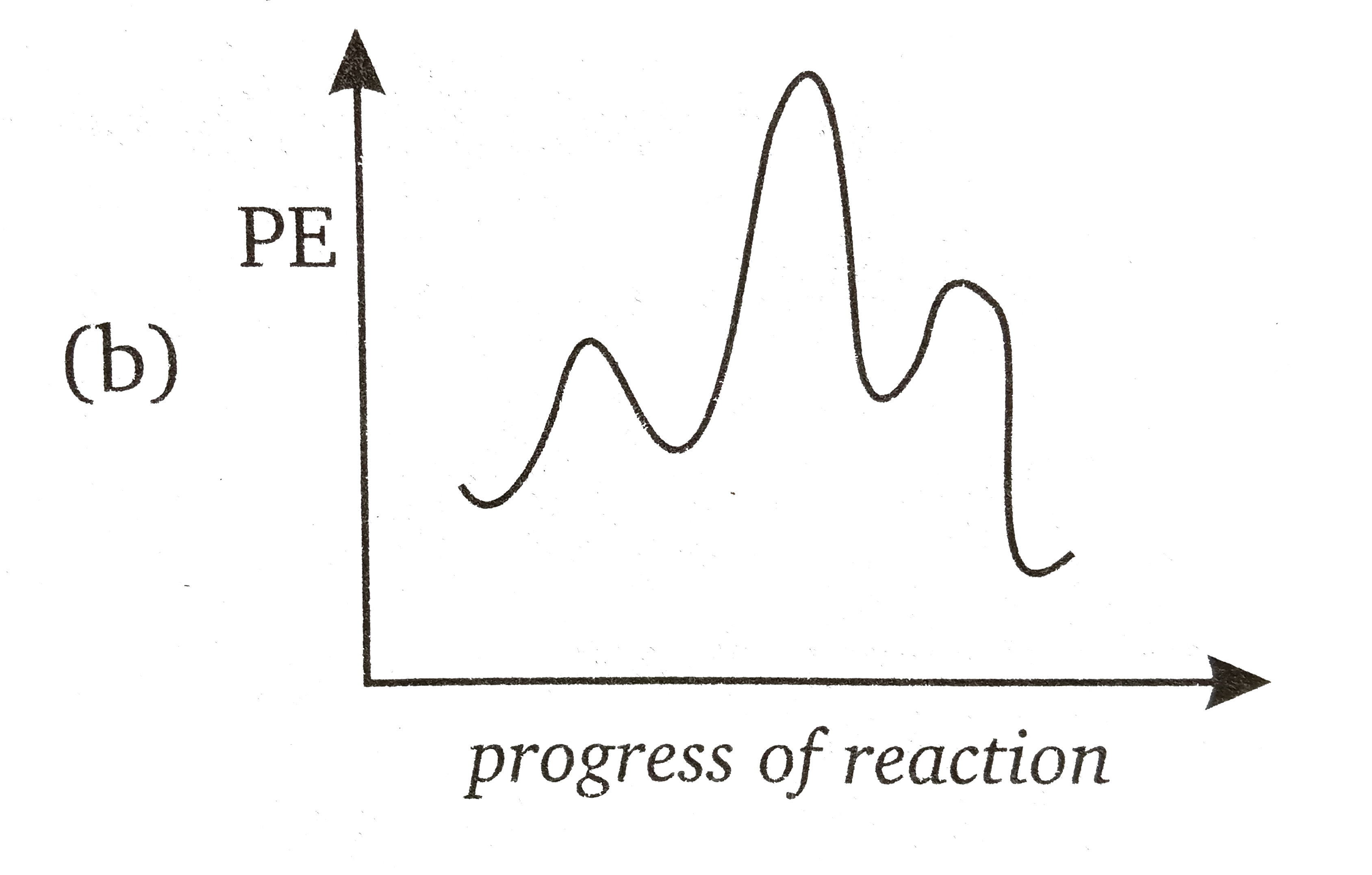
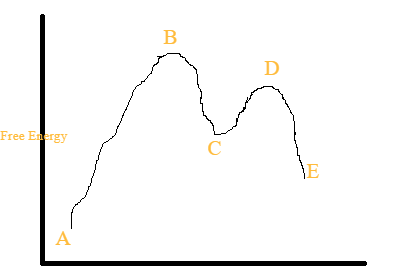
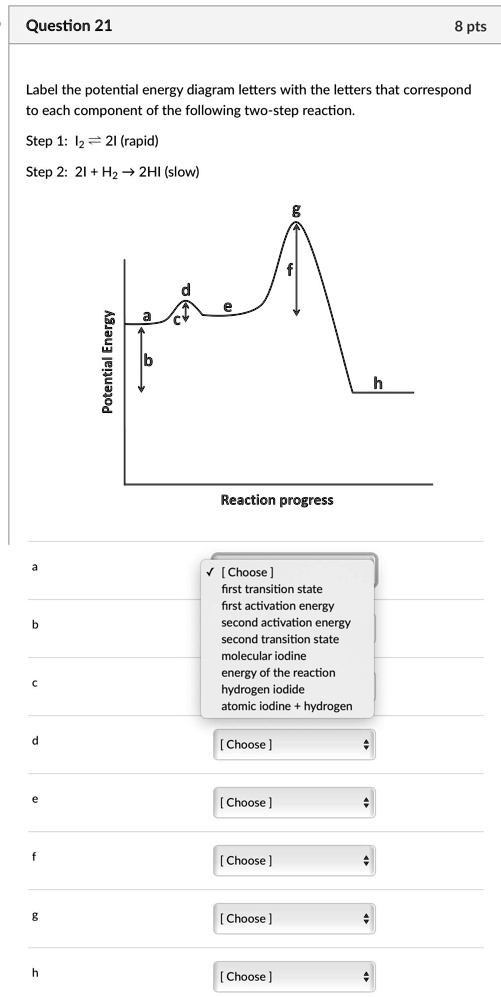
Energy Diagrams of Reactions | Fiveable To find the activation energy, you should be looking for two numbers: the potential energy of the reactants and the energy of the activated complex (the maximum point). (energy of activation complex) - (PEreactants) (100 kJ) - (40 kJ) = 60 kJ In other words, it takes 60 kJ of energy to complete the reaction. How do you find the rate determining step from a graph? The rate determining step in a reaction mechanism is the slowest step. It is characterized by its high activation energy. Consider the energy diagram represented below of a two-step mechanism. The first step is the slow step since it has the highest activation energy. Here is more about this topic in the following video: Chemical Kinetics ... Energy Diagrams: Describing Chemical Reactions Draw an energy diagram for a two-step reaction that is exothermic overall, and consists of a fast but endothermic first step, and a slow but exothermic second step. Indicate DGrxn, as well as DG1* and DG2* for the first and second activation energies, respectively. Label the positions corresponding to the transition states with an asterisk. PDF Unit 5 - Kinetics - Chemistry Teaching Resources Step 1: NO. 2 + F. 2 . → NO. 2. F + F (slow) Step 2: NO. 2 + F → NO. 2. F (fast) a) rite a rate law for the overall reaction that is consistent with the proposed W mechanism. rate = k [NO. 2] [F. 2] b) On the incomplete reaction energy diagram below, draw a curve that shows the . following two details. The relative activation energies of ...
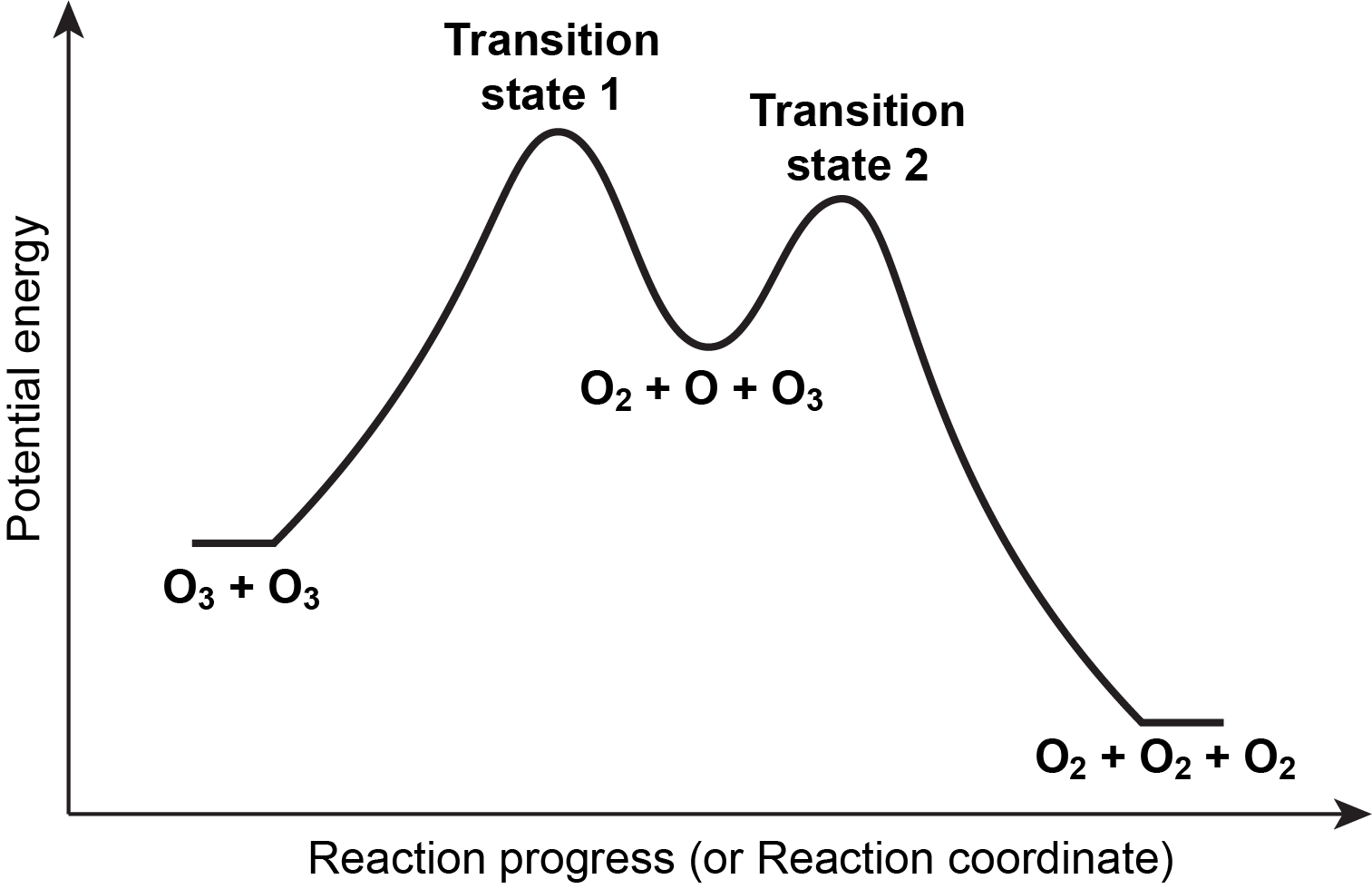
Multistep Reactions - Softschools.com The energy diagram of a two-step reaction is shown below. In the above reaction, a reactant goes through one elementary step with a lower activation energy (transition state 1) to form the intermediate. The intermediate then goes through a second step (transition state 2) with the highest energy barrier to form the product. Potential Energy Diagrams - Kentchemistry.com Answer-->. KNO 3 NH 4 Cl NH 4 NO 3 NaCl. 6/04. 21 A catalyst increases the rate of a chemical reaction by. (1) lowering the activation energy of the reaction (2) lowering the potential energy of the products. (3) raising the temperature of the reactants (4) raising the concentration of the reactants. Answer-->. Mechanisms and Potential Energy Diagrams | Chemistry for Non-Majors ... A potential energy diagram for a two-step reaction is shown and labeled. Practice View the section on two-step reactions at the site below and then do the self-test (both buttons are at the top of the slide). Don't worry about - just consider it an indication of activation energy as is in the diagram above. 6.15: Energy Diagram for a Two-Step Reaction Mechanism Recall that the first step of the reaction above, in which two charged species are formed from a neutral molecule, is much the slower of the two steps, and is therefore rate-determining. This is illustrated by the energy diagram, where the activation energy for the first step is higher than that for the second step.
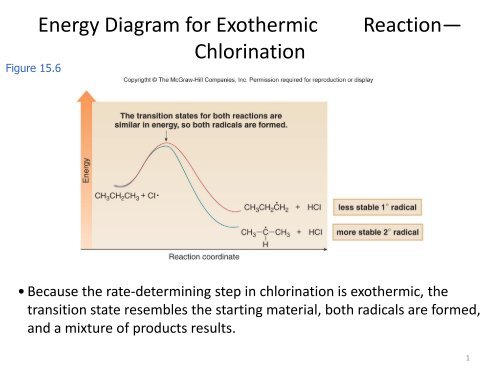
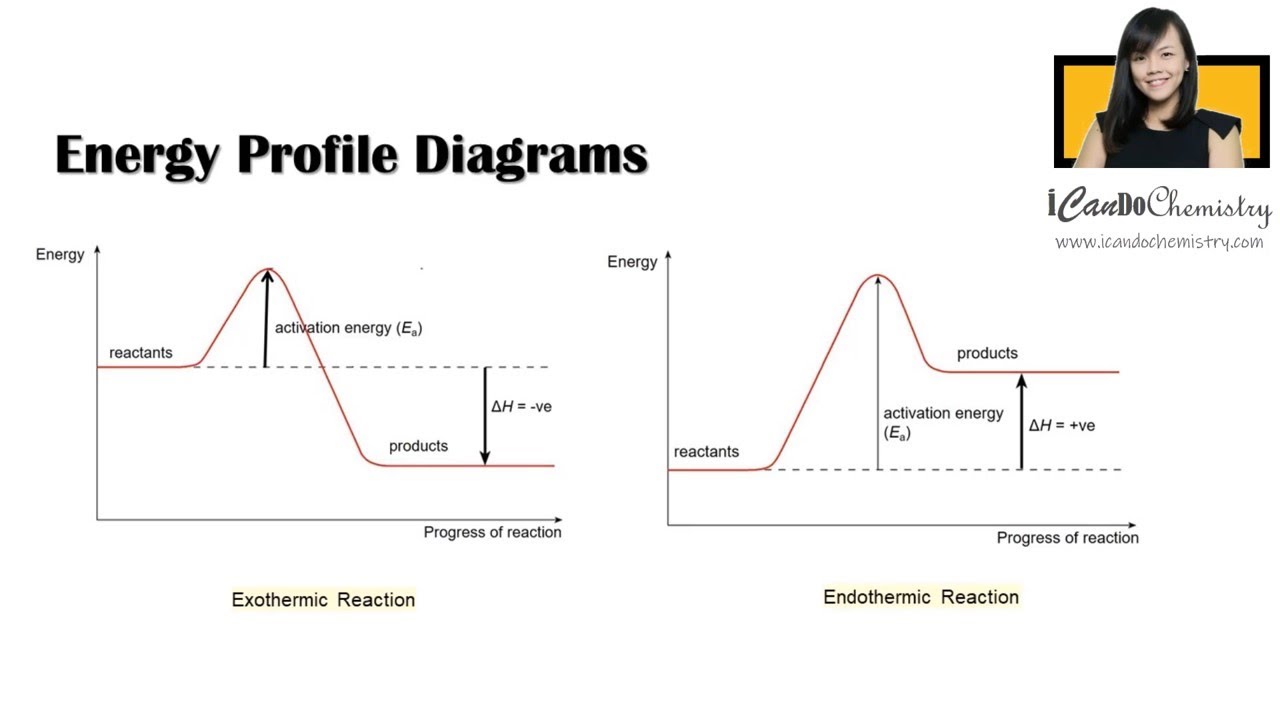
7.2 SN2 Reaction Mechanisms, Energy Diagram and Stereochemistry The energy changes for the above reaction can be represented in the energy diagram shown in Fig. 7.1. S N 2 is a single-step reaction, so the diagram has only one curve. The products CH 3 OH and Br - are in a lower energy than the reactants CH 3 Br and OH -, which indicates that the overall reaction is exothermic and the products are more stable.
CH 368: Unit 2 - University of Texas at Austin 1. The Basic Equation. According to transition state theory, the rates of reactions are given by the following equation: where k is the rate constant for a given reaction, k is Boltzmann's constant, T is the absolute temperature, h is Planck's constant, and DG* is the free energy difference between the transition state and the reactants, i ...
Multistep reaction energy profiles (video) - Khan Academy Next we're ready for the second hill or the second step of our mechanism. In the second step, AC the intermediate AC reacts with D to form A and CD. So the top of this second hill would be the transition state for this second step. So we can show the bond between A and C braking, and at the same time the bond between C and D is forming.
Draw an energy diagram for a two-step exergonic reaction whose second ... That means that the activation energy, the second step Yes, last time, the activation energy of the first. Okay, so, no, that's represent, that's and on energy diagram. Okay, so we have two steps that we need to be accountable. So now let's just start 12 with the reactions. You know, that's draw the first step of the action.
Potential Energy Diagrams - Chemistry - YouTube This chemistry video tutorial focuses on potential energy diagrams for endothermic and exothermic reactions. It also shows the effect of a catalyst on the f...
Energy Diagrams of Two Step Reactions - YouTube Watch Complete videos @ Organic Chemistry 1
Energy Diagram - Organic Chemistry Video | Clutch Prep Video explaining Energy Diagram for Organic Chemistry. ... Free energy diagrams show overall changes in potential energy during reactions. ... Determined by Gibbs Free Energy (ΔG ° = ΔH ° - TΔS). Kinetics describes rate. Determined by the activation energy of the rate determining step (E a). Example #1: Describe the favorability and rate ...
Answered: Sketch an energy diagram for a two-step… | bartleby To draw: An energy diagram for a two-step reaction in which both steps are exergonic and in which the second step has a higher-energy transition state than the first. Label the parts of the diagram correspoding to reactant, product, intermediate, overall ΔG‡, and overall ΔG°. arrow_forward
Draw an energy diagram for a two-step reaction, - Quizlet Find step-by-step Chemistry solutions and your answer to the following textbook question: Draw an energy diagram for a two-step reaction, $$ A \rightarrow B \rightarrow C, $$ where the relative energy of these compounds is C < A < B, and the conversion of $$ B \rightarrow C $$ is rate-determining..
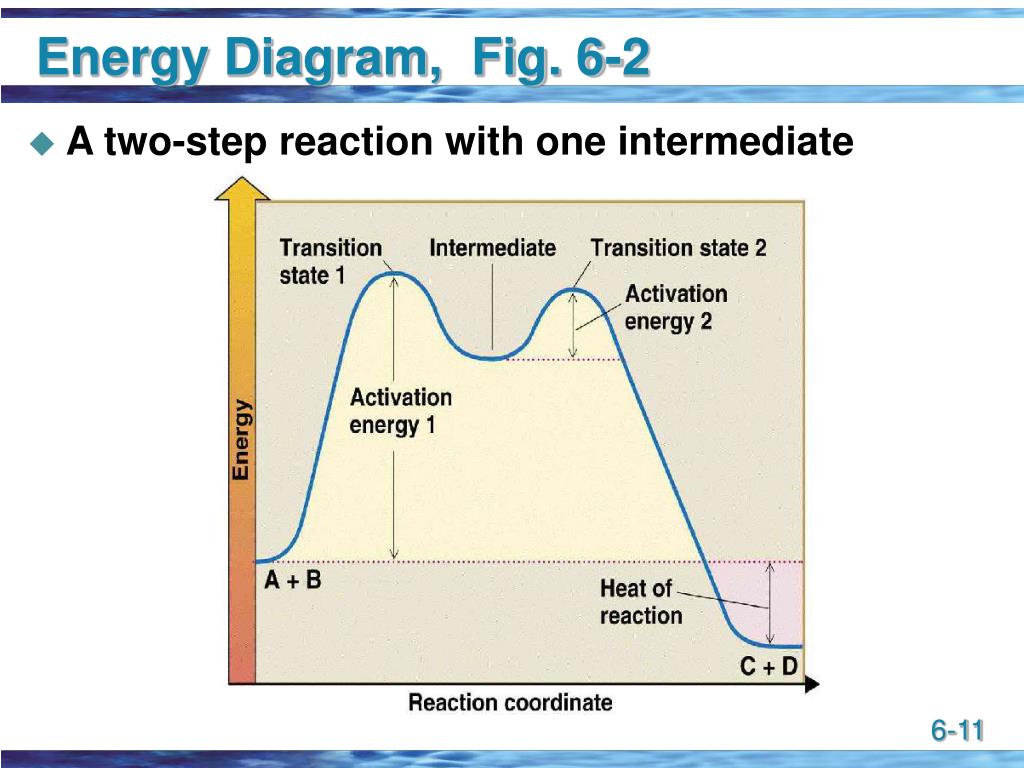
Energy Diagram for a Two-Step Reaction Mechanism Complete Energy Diagram for Two-Step Reaction A Two-Step Reaction Mechanism The transition states are located at energy maxima. The reactive intermediate B+ is located at an energy minimum. Each step has its own delta H and activation energy. The overall energy difference between the starting materials and products is delta H overall.
Solved: Sketch an energy diagram for a two-step reaction in which ... 13P Sketch an energy diagram for a two-step reaction in which both steps are exergonic and in which the second step has a higher-energy transition state than the first. Label the parts of the diagram corresponding to reactant, product, intermediate, overall Δ G‡, and overall Δ G °. Step-by-step solution 89% (9 ratings) for this solution Step 1 of 4
7.4 SN1 Reaction Mechanisms, Energy Diagram and Stereochemistry 7.4 SN1 Reaction Mechanisms, Energy Diagram and Stereochemistry SN1 Reaction Mechanism The reaction between tert -butylbromide and water proceeds via the SN1 mechanism. Unlike S N 2 which is a single-step reaction, S N 1 reaction involves multiple steps. Reaction: (CH 3) 3 CBr + H 2 O → (CH 3) 3 COH + HBr
12.7 Catalysis - Chemistry - opentextbc.ca Figure 2. This potential energy diagram shows the effect of a catalyst on the activation energy. ... provides a different reaction path with a lower activation energy. As shown, the catalyzed pathway involves a two-step mechanism (note the presence of two transition states) and an intermediate species (represented by the valley between the two ...

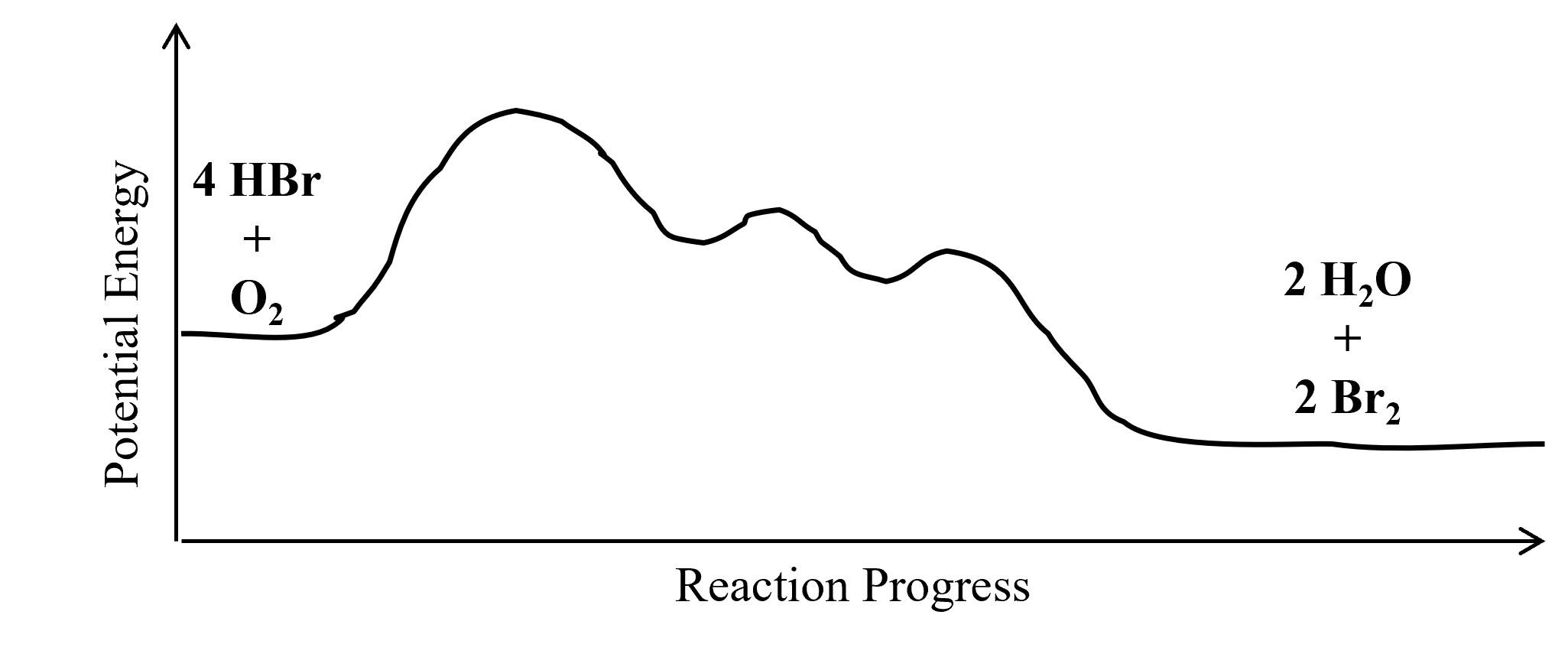
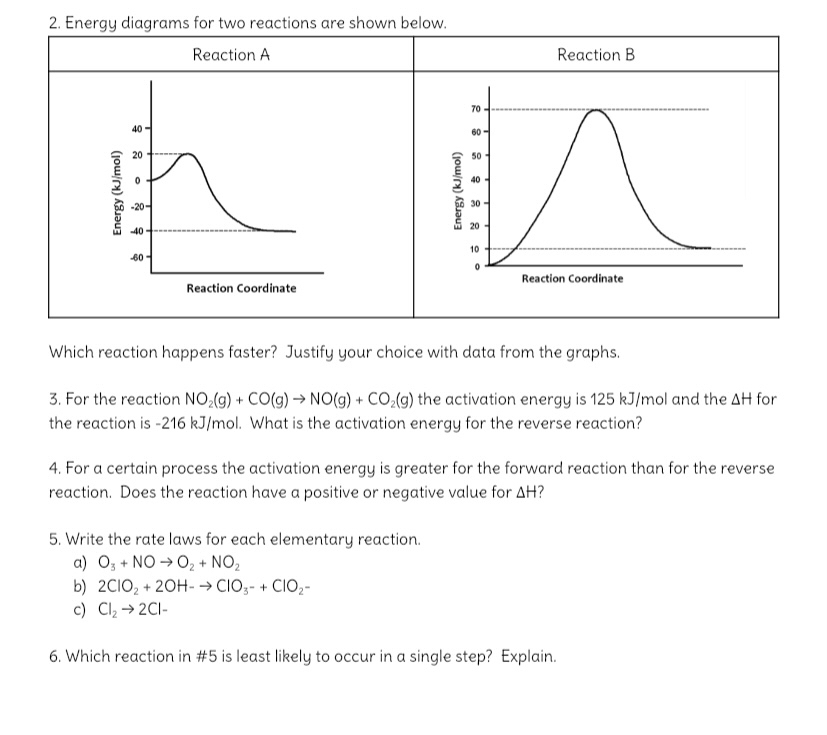


















Post a Comment for "45 2 step reaction energy diagram"